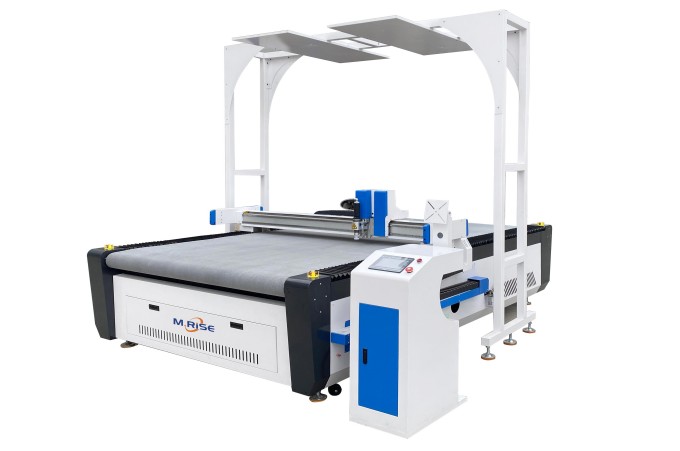
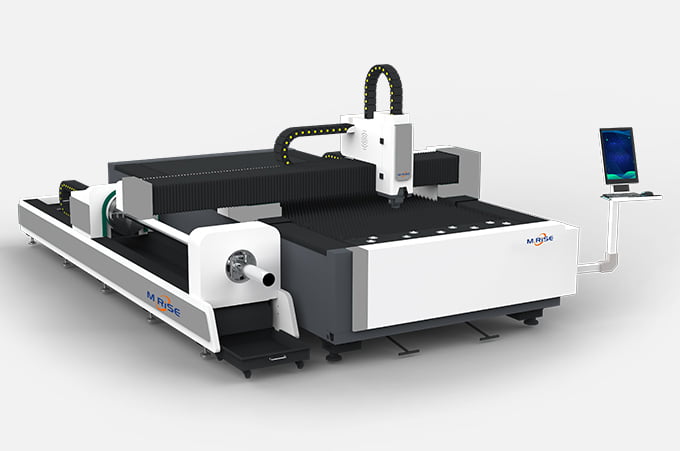
- Technical principle
Laser cutting uses a focused high-power density (exceeding the material threshold) laser beam to irradiate the workpiece. The energy of the laser beam and the chemical reaction heat energy added by the active gas-assisted cutting process are all absorbed by the material, causing the temperature of the laser action point to rise sharply. After reaching the boiling point or melting point, the material begins to vaporize or melt and form holes. With the relative movement of the laser beam and the workpiece, the material eventually forms an incision, and the slag at the incision is blown away by a certain auxiliary airflow, thereby realizing a thermal cutting method of cutting the workpiece.

- Commonly used materials
At present, there are two main types of laser cutting machines on the market: laser cutting machines with carbon dioxide lasers and laser cutting machines with fiber lasers. Compared with carbon dioxide lasers, fiber lasers have a high photoelectric conversion rate and low maintenance costs, so they are recognized by more companies and laser processing users. At present, fiber laser cutting machines are more widely used in the market.

Fiber laser cutting machines can only be used to cut metals, not non-metals. Commonly used materials for cutting are stainless steel, carbon steel, aluminum alloy, brass, copper, etc., among which copper is a high-reflective material. Highly reflective materials will affect the performance of the laser, and long-term cutting will shorten the service life of the cutting machine.